|
I am a fourth year PhD. student at IIT Delhi, where I work in the Laboratory for Computational Social Systems (LCS2) lead by Dr. Tanmoy Chakraborty. My primary area of research includes understanding generalization capabilities of small and efficient language models. I lead the Parmanu (Atomic) group within LCS2, which explores efficient architectures, fine‑tuning, inference, model compression and scaling laws to make large language models accessible on commodity hardware. I work as a Principal Data Scientist at Optum, the intelligence arm of UnitedHealth Group, where I lead AI‑first solutions for the Home & Community business, building generative and predictive models that improve patient care and operations. Over the past eight years I’ve progressed from Data Scientist through Senior and Lead roles, guiding cross‑functional teams and deploying scalable predictive modelling and AI/ML projects. As a Master Inventor with seven granted U.S. patents, I serve on Optum’s Patent Review Board and mentor early‑stage inventors. The platforms I’ve built deliver more than $20 million in annual value, highlighting the tangible impact of data science in healthcare. I completed my Masters in Business Analytics and Data Science (PGDBA) from Indian Institute of Management, Calcutta . Prior to that, I did my Masters of Science in Mathematics and Computing from Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati in 2015 and Bachelor of Science in Mathematics and Computer Science from Chennai Mathematical Institute in 2013. |

|
| News · Experience · Research Portfolio · Selected Publications · Granted Patents · Competitions & OSS · Education · Extra · |

|
|
|
||
|
Principal Data Scientist at UnitedHealth Group with 8+ years of experience and numerous innovation awards and patents. |
Focused on efficient large language models, low‑resource language modelling and persona‑aware generative modelling. |
Bronze medalist in multiple Kaggle competitions and creator of an open‑source JST library. |
|
|
|
Lead the design of AI‑first solutions for home and community business of OptumHealth within a 6-member team. Member of TLCP (top 0.1%) program. Member of the company’s patent review board, mentoring early stage inventors; recognised with the Master Inventor award for contributing to several U.S. patents. |
|
|
Earned Master Inventor recognition and served on the patent review board. Advanced predictive modelling and natural‑language processing projects. Built and deployed data‑driven models for customer analytics. Honoured with the 2018 Q4 R&R Mastermind award and third place in a company‑wide analytics championship. |
|
|
|
My research advances a paradigm shift from indiscriminate scaling toward downscaling large language models, aiming to make them efficient, sustainable, and deployable under real-world constraints. I work on principled methods for model compression, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, KV-cache compression, and test-time compute optimization, complemented by theoretical and empirical studies on scaling and pruning laws. Collectively, this line of work seeks to preserve model capability while significantly reducing memory footprint, latency, and energy consumption. To support multilingual and under-represented language communities, I design robust representation learning methods for low-resource, code-mixed, and code-switched languages. My work introduces hierarchical and linguistically informed architectures that capture cross-lingual structure and social context, improving performance on tasks such as sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and language identification. I also study computational linguistic frameworks to understand the evolution, structure, and dynamics of code-mixed language in natural settings. In generative modelling, I develop persona-aware and probabilistic models that generate socially and linguistically realistic text, particularly for code-mixed and multilingual settings. This includes Transformer-based encoder–decoder architectures that incorporate user persona, context, and alignment objectives, as well as earlier work on interpretable generative models for aspect-based opinion mining and sentiment analysis. These models aim to bridge expressiveness, controllability, and real-world linguistic validity. |
|
All publications are available on Google Scholar. |
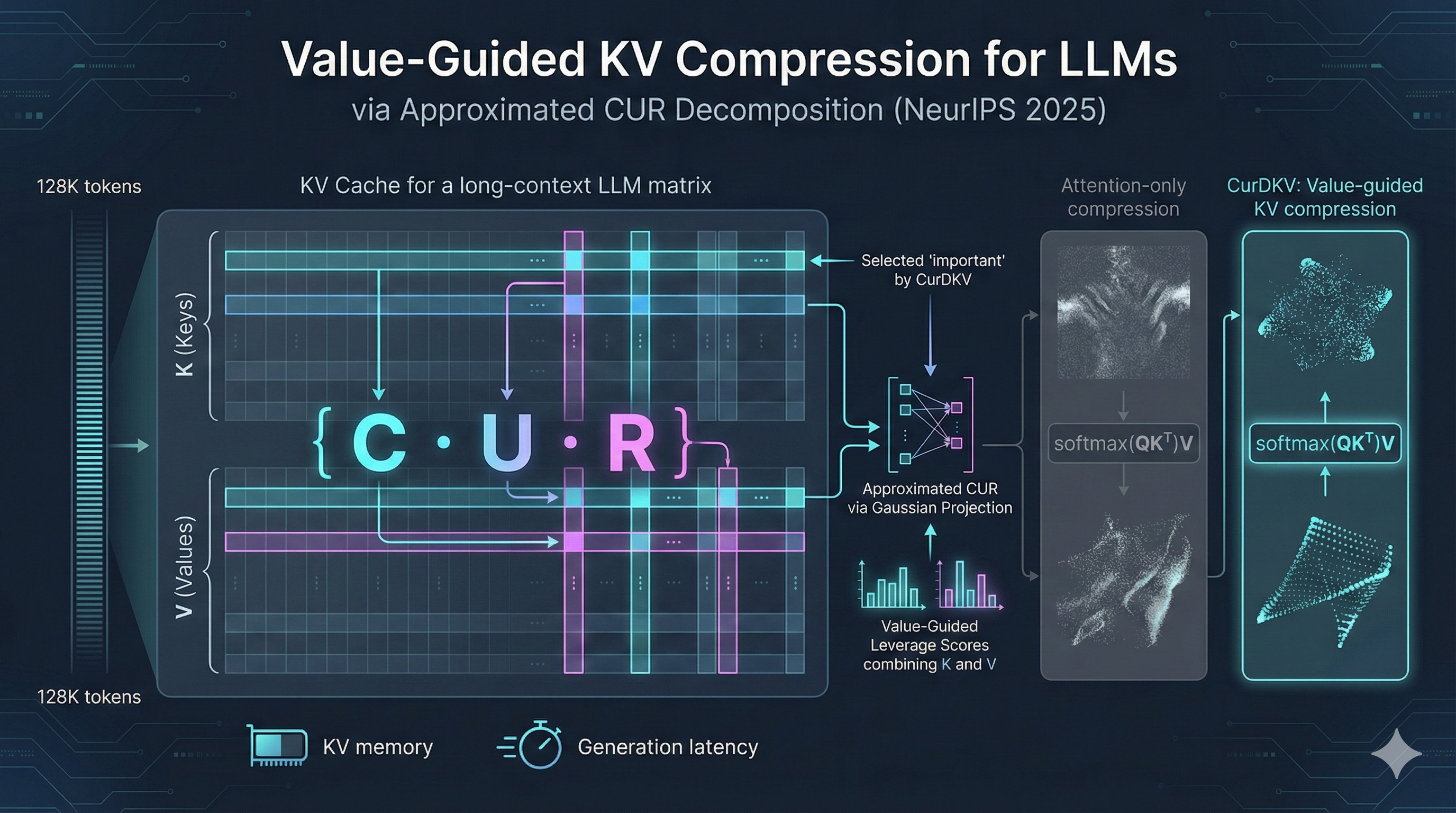
|
Key-value (KV) cache compression has emerged as a critical technique for reducing the memory and latency overhead of autoregressive language models during inference. Prior approaches predominantly rely on query-key attention scores to rank and evict cached tokens, assuming that attention intensity correlates with semantic importance. However, this heuristic overlooks the contribution of value vectors, which directly influence the attention output. In this paper, we propose CurDKV, a novel, value-centric KV compression method that selects keys and values based on leverage scores computed from CUR matrix decomposition. Our approach approximates the dominant subspace of the attention output , ensuring that the retained tokens best preserve the model's predictive behavior. Theoretically, we show that attention score approximation does not guarantee output preservation, and demonstrate that CUR-based selection minimizes end-to-end attention reconstruction loss. Empirically, CurDKV achieves up to 9.6% higher accuracy than state-of-the-art methods like SnapKV and ChunkKV under aggressive compression budgets on LLaMA and Mistral, while maintaining compatibility with FlashAttention and Grouped Query Attention. In addition to improved accuracy, CurDKV reduces generation latency by up to 40% at high compression, offering a practical speed-accuracy tradeoff. |
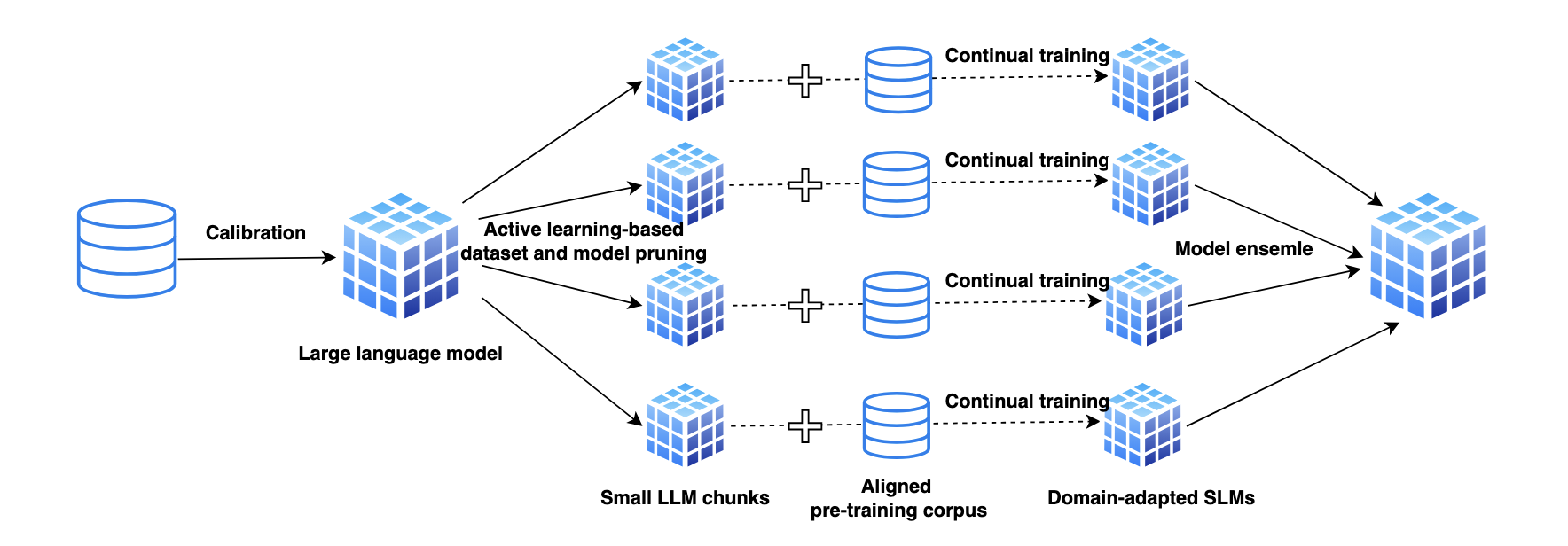
|
We challenge the dominant focus on neural scaling laws and advocate for a paradigm shift toward downscaling in the development of large language models (LLMs). While scaling laws have provided critical insights into performance improvements through increasing model and dataset size, we emphasize the significant limitations of this approach, particularly in terms of computational inefficiency, environmental impact, and deployment constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a holistic framework for downscaling LLMs that seeks to maintain performance while drastically reducing resource demands. This paper outlines practical strategies for transitioning away from traditional scaling paradigms, advocating for a more sustainable, efficient, and accessible approach to LLM development. |
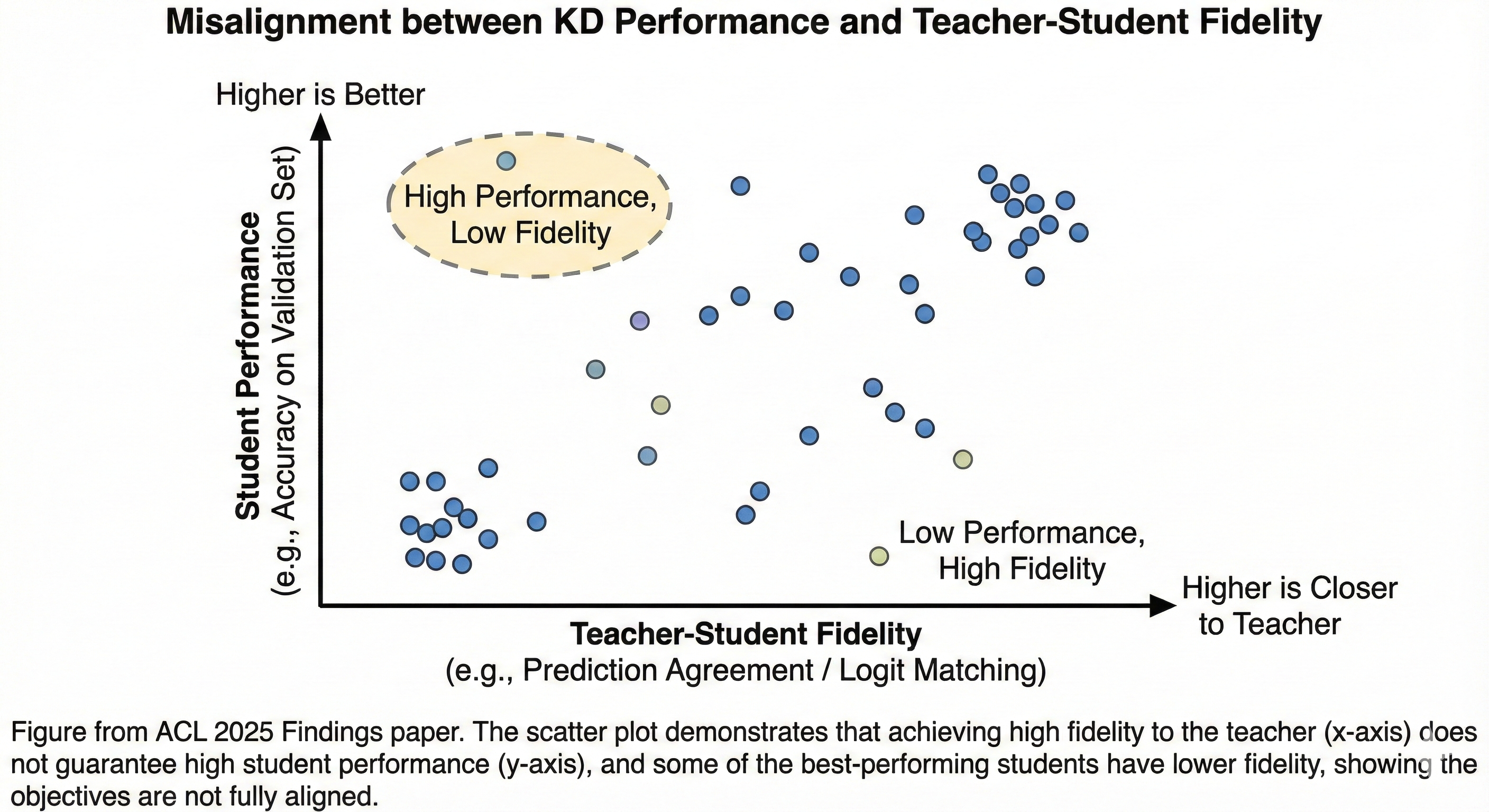
|
Knowledge distillation (KD) is a key technique for compressing large language models into smaller ones while preserving performance. Despite the recent traction of KD research, its effectiveness for smaller language models (LMs) and the mechanisms driving knowledge transfer remain underexplored. In this work, we present the first large-scale empirical and statistical analysis of KD across models ranging from 0.5B to 7B parameters on 14 complex reasoning tasks in a zero-shot setting. Our findings reveal that KD can improve the average performance of smaller models by up to 10%, with a peak task specific gain of 22%, while providing only marginal benefits (∼ 1.3%) for larger models. Surprisingly, teacher performance has a minimal impact on student outcomes, while teacher task expertise impacts KD effectiveness. A correlation study indicates that smaller LMs benefit more from KD, whereas larger LMs show diminished gains. Additionally, we uncover a misalignment between improvements in student performance and reasoning fidelity, suggesting that while KD enhances accuracy, it does not always maintain the structured decision-making processes of the teacher. Our ablation study further highlights the importance of teacher signals and logit smoothing in influencing students’ performance after distillation. Overall, our study offers a comprehensive empirical and statistical assessment of KD, highlighting both its benefits and trade-offs when distilling knowledge from larger to smaller LMs. |
|
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on downstream tasks requires substantial computational resources. Selective-PEFT, a class of parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methodologies, aims to mitigate these computational challenges by selectively fine-tuning only a small fraction of the model parameters. Although parameter-efficient, these techniques often fail to match the performance of fully fine-tuned models, primarily due to inherent biases introduced during parameter selection. Traditional selective-PEFT techniques use a fixed set of parameters selected using different importance heuristics, failing to capture parameter importance dynamically and often leading to suboptimal performance. We introduce ID3, a novel selective-PEFT method that calculates parameter importance continually, and dynamically unmasks parameters by balancing exploration and exploitation in parameter selection. Our empirical study on 16 tasks spanning natural language understanding, mathematical reasoning, and summarization demonstrates the effectiveness of our method compared to fixed-masking selective-PEFT techniques. We analytically show that ID3 reduces the number of gradient updates by a factor of two, enhancing computational efficiency. Since ID3 is robust to random initialization of neurons and operates directly on the optimization process, it is highly flexible and can be integrated with existing additive and reparameterization-based PEFT techniques such as Adapters and LoRA, respectively |

|
Large Language Models (LLMs) are highly resource-intensive to fine-tune due to their enormous size. While low-rank adaptation is a prominent parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach, it suffers from sensitivity to hyperparameter choices, leading to instability in model performance on fine-tuning downstream tasks. This paper highlights the importance of effective parameterization in low-rank fine-tuning to reduce estimator variance and enhance the stability of final model outputs. We propose MonteCLoRA, an efficient fine-tuning technique that employs Monte Carlo estimation to learn an unbiased posterior estimation of low-rank parameters with low expected variance, stabilizing fine-tuned LLMs with only O(r) additional parameters, for a given rank r. MonteCLoRA shows 0.5% and 1.6% improvements in accuracy and robustness over unregularized low-rank adaptation method on natural language understanding tasks with pre-trained RoBERTa-base. Furthermore, in generative tasks with pre-trained LLaMA-1-7B and LLaMA-3.2-3B-Instruct, MonteCLoRA demonstrates robust performance with 50% and 62% lower spreads respectively than the contemporary efficient fine-tuning methods. The theoretical and empirical results presented in the paper underscore how parameterization and hyperpriors balance exploration-exploitation in the low-rank parametric space, therefore leading to more optimal and robust parameter estimation during efficient fine-tuning. |
|
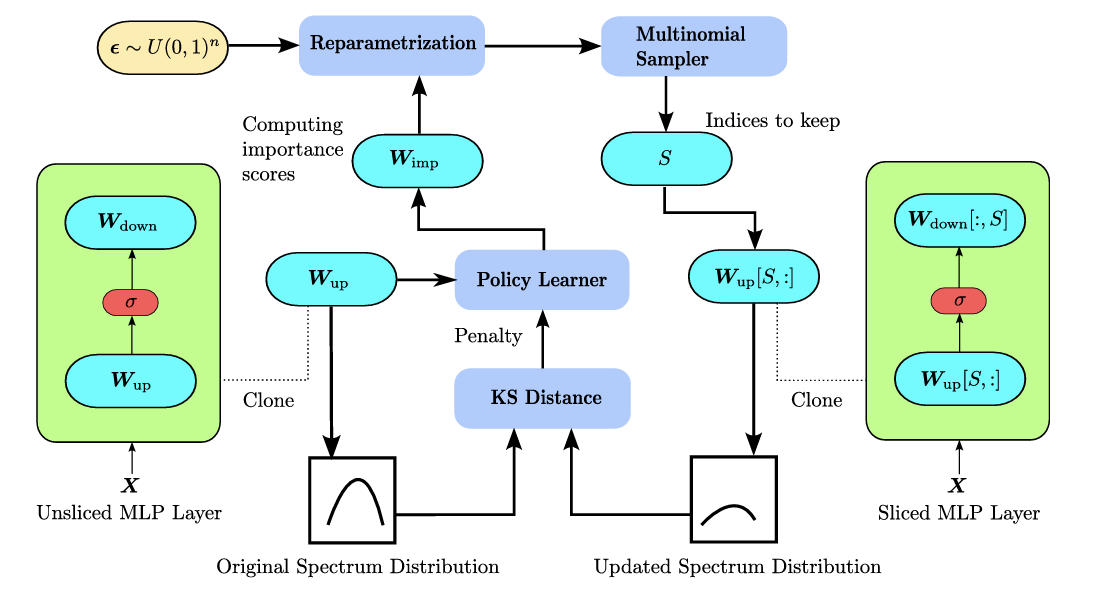
The ever-increasing size of large language models (LLMs) presents significant challenges for deployment due to their heavy computational and memory requirements. Current model pruning techniques attempt to alleviate these issues by relying heavily on external calibration datasets to determine which parameters to prune or compress, thus limiting their flexibility and scalability across different compression ratios. Moreover, these methods often cause severe performance degradation, particularly in downstream tasks, when subjected to higher compression rates. In this paper, we propose PruneNet, a novel model compression method that addresses these limitations by reformulating model pruning as a policy learning process. PruneNet decouples the pruning process from the model architecture, eliminating the need for calibration datasets. It learns a stochastic pruning policy to assess parameter importance solely based on intrinsic model properties while preserving the spectral structure to minimize information loss. PruneNet can compress the LLaMA-2-7B model in just 15 minutes, achieving over 80% retention of its zero-shot performance with a 30% compression ratio, outperforming existing methods that retain only 75% performance. Furthermore, on complex multitask language understanding tasks, PruneNet demonstrates its robustness by preserving up to 80% performance of the original model, proving itself a superior alternative to conventional structured compression techniques. |
|
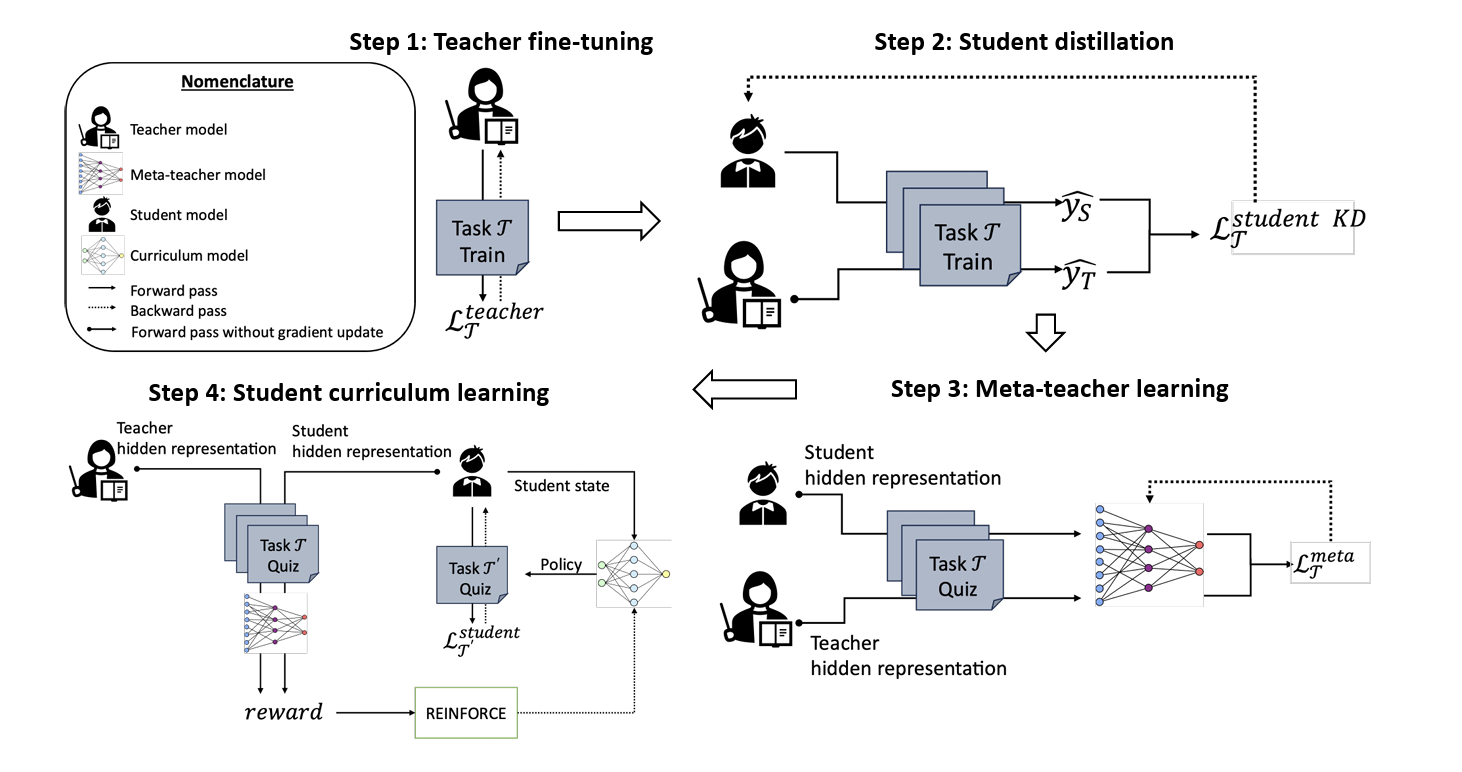
Knowledge distillation (KD) is a technique used to transfer knowledge from a larger “teacher” model into a smaller “student” model. Recent advancements in meta-learning-based knowledge distillation (MetaKD) emphasize that the finetuning of teacher models should be aware of the student’s need to achieve better knowledge distillation. However, existing MetaKD methods often lack incentives for the teacher model to improve itself. In this study, we introduce MPDistil, a meta-policy distillation technique, that utilizes novel optimization strategies to foster both collaboration and competition during the fine-tuning of the teacher model in the meta-learning step. Additionally, we propose a curriculum learning framework for the student model in a competitive setup, in which the student model aims to outperform the teacher model by self-training on various tasks. Exhaustive experiments on SuperGLUE and GLUE benchmarks demonstrate the efficacy of MPDistil compared to 20 conventional KD and advanced MetaKD baselines, showing significant performance enhancements in the student model– e.g., a distilled 6-layer BERT model outperforms a 12-layer BERT model on f ive out of six SuperGLUE tasks. Furthermore, MPDistil, while applied to a large language teacher model (DeBERTa-v2-xxlarge), significantly narrows the performance gap of its smaller student counterpart (DeBERTa-12) by just 4.6% on SuperGLUE. Wefurther demonstrate how higher rewards and customized training curricula strengthen the student model and enhance generalizability. |
|
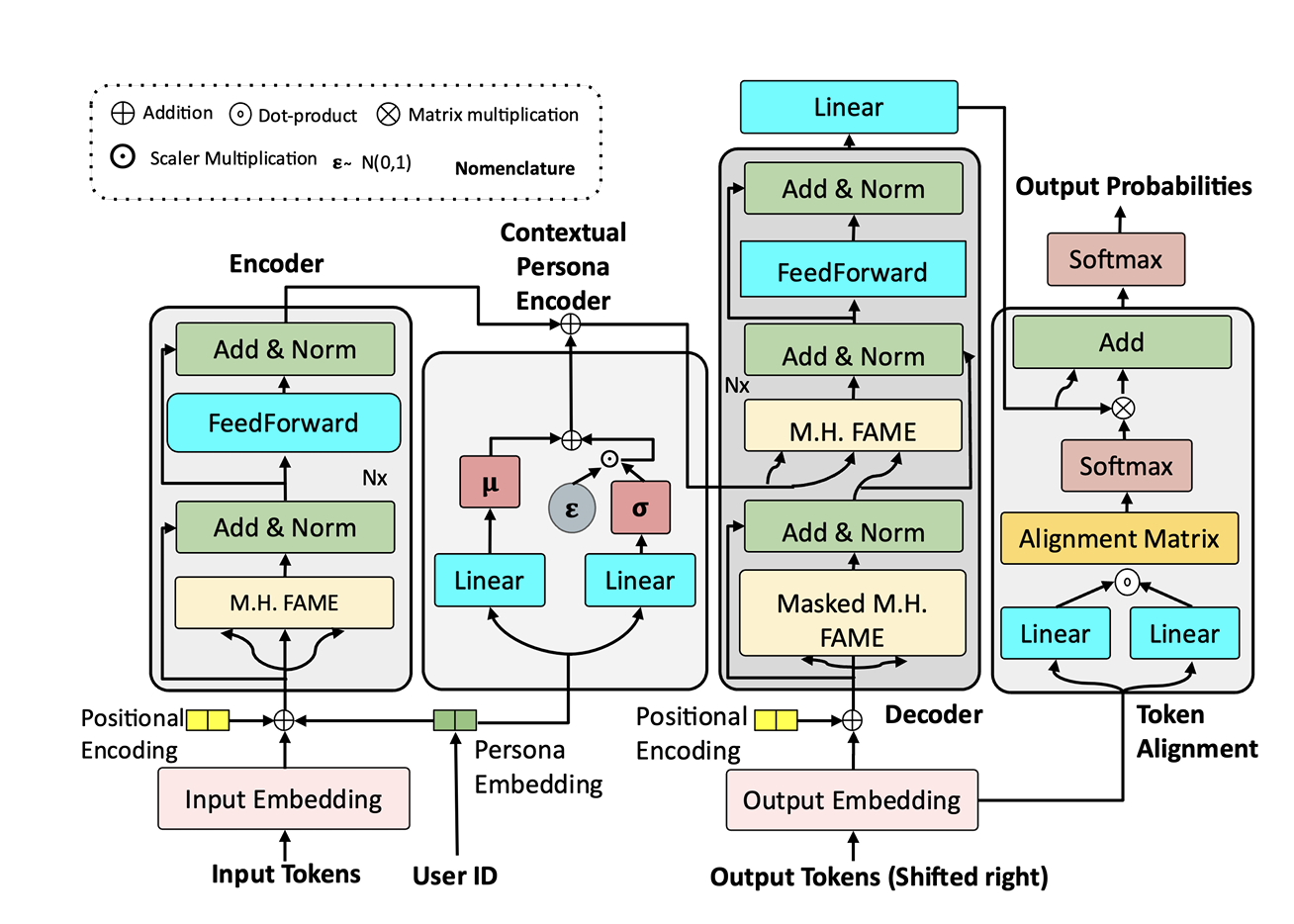
Code-mixing and script-mixing are prevalent across online social networks and multilingual societies. However, a user’s preference toward code-mixing depends on the socioeconomic status, demographics of the user, and the local context, which existing generative models tend to ignore while generating code-mixed texts. In this work, we make a pioneering attempt to develop a persona-aware generative model to generate texts resembling real-life code-mixed texts of individuals. We propose PARADOX, a persona-aware generative model for code-mixed text generation, which is a novel Transformer-based encoder-decoder model that encodes an utterance conditioned on a user’s persona and generates code-mixed texts without monolingual reference data. We propose an alignment module that re-calibrates the generated sequence to resemble real-life code-mixed texts. PARADOX generates code-mixed texts that are semantically more meaningful and linguistically more valid. To evaluate the personification capabilities of PARADOX, we propose four new metrics– CM BLEU, CM Rouge-1, CM Rouge-L and CM KS. On average, PARADOX achieves 1.6% better CM BLEU, 57% better perplexity and 32% better semantic coherence than the non-persona-based counterparts. |
|
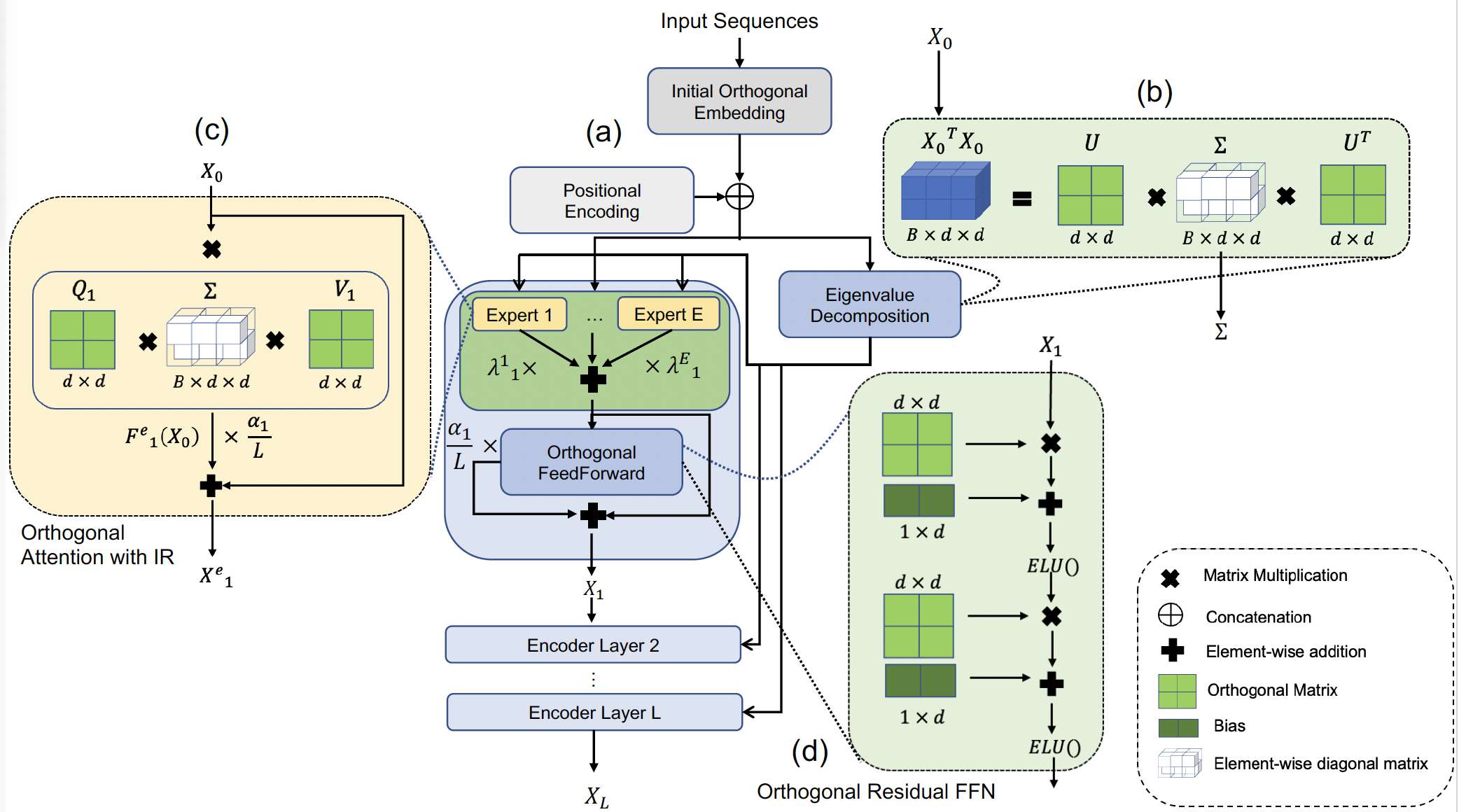
Multi-head self-attention-based Transformers have shown promise in different learning tasks. Albeit these models exhibit significant improvement in understanding short-term and long-term contexts from sequences, encoders of Transformers and their variants fail to preserve layer-wise contextual information. Transformers usually project tokens onto sparse manifolds and fail to preserve mathematical equivalence among the token representations. In this work, we propose TransJect, an encoder model that guarantees a theoretical bound for layer-wise distance preservation between a pair of tokens. We propose a simple alternative to dot-product attention to ensure Lipschitz continuity. This allows TransJect to learn injective mappings to transform token representations to different manifolds with similar topology and preserve Euclidean distance between every pair of tokens in subsequent layers. Evaluations across multiple benchmark short- and long-sequence classification tasks show maximum improvements of 6.8% and 5.9%, respectively, over the variants of Transformers. Additionally, TransJect displays 79% better performance than Transformer on the language modeling task. We further highlight the shortcomings of multi-head self-attention from the statistical physics viewpoint. Although multi-head self-attention was incepted to learn different abstraction levels within the networks, our empirical analyses suggest that different attention heads learn randomly and unorderly. In contrast, TransJect adapts a mixture of experts for regularization; these experts are more orderly and balanced and learn different sparse representations from the input sequences. TransJect exhibits very low entropy and can be efficiently scaled to larger depths. |

Image Credits: Link |
Aggression is a prominent trait of human beings that can affect social harmony in a negative way. The hate mongers misuse the freedom of speech in social media platforms to flood with their venomous comments in many forms. Identifying different traits of online offense is thus inevitable and the need of the hour. Existing studies usually handle one or two offense traits at a time, mainly due to the lack of a combined annotated dataset and a scientific study that provides insights into the relationship among the traits. In this paper, we study the relationship among five offense traits – aggression, hate, sarcasm, humor, and stance in Hinglish (Hindi-English) social media code-mixed texts. We employ various state-of-the-art deep learning systems at different morphological granularities for the classification across five offense traits. Our evaluation of the unified framework suggests performance across all major traits. Furthermore, we propose a novel notion of causal importance score to quantify the effect of different abusive keywords and the overall context on the offensiveness of the texts. |

Image Credits: Link |
Understanding linguistics and morphology of resource-scarce code-mixed texts remains a key challenge in text processing. Although word embedding comes in handy to support downstream tasks for low-resource languages, there are plenty of scopes in improving the quality of language representation particularly for code-mixed languages. In this paper, we propose HIT, a robust representation learning method for code-mixed texts. HIT is a hierarchical transformer-based framework that captures the semantic relationship among words and hierarchically learns the sentence-level semantics using a fused attention mechanism. HIT incorporates two attention modules, a multi-headed self-attention and an outer product attention module, and computes their weighted sum to obtain the attention weights. Our evaluation of HIT on one European (Spanish) and five Indic (Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam) languages across four NLP tasks on eleven datasets suggests significant performance improvement against various state-of-the-art systems. We further show the adaptability of learned representation across tasks in a transfer learning setup (with and without fine-tuning). |
Image Credits: Link |
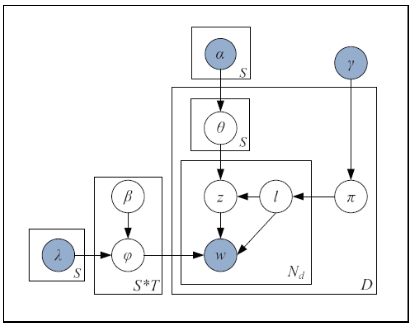
Short text is a popular avenue of sharing feedback, opinions and reviews on social media, e-commerce platforms, etc. Many companies need to extract meaningful information (which may include thematic content as well as semantic polarity) out of such short texts to understand users’ behaviour. However, obtaining high quality sentiment-associated and human interpretable themes still remains a challenge for short texts. In this paper we develop ELJST, an embedding enhanced generative joint sentiment-topic model that can discover more coherent and diverse topics from short texts. It uses Markov Random Field Regularizer that can be seen as generalisation of skip-gram based models. Further, it can leverage higher order semantic information appearing in word embedding, such as self-attention weights in graphical models. Our results show an average improvement of 10% in topic coherence and 5% in topic diversification over baselines. Finally, ELJST helps understand users' behaviour at more granular levels which can be explained. All these can bring significant values to service and healthcare industries often dealing with customers. |
|
|
|

|
In this challenge, the participants were asked to write an essay on one of the following seven chosen topics from the field of AI, with a prompt to describe what the community has learned over the past 2 years of working and experimenting with.
|

|
In this challenge, the objective is to classify whether a comment is toxic (or, abusive). The dataset contains multi-lingual comments from different Wikipedia talk pages. We experimented with various multilingual transformer models, Universal Sentence Encoder (USE) and their ensembles.
|
|
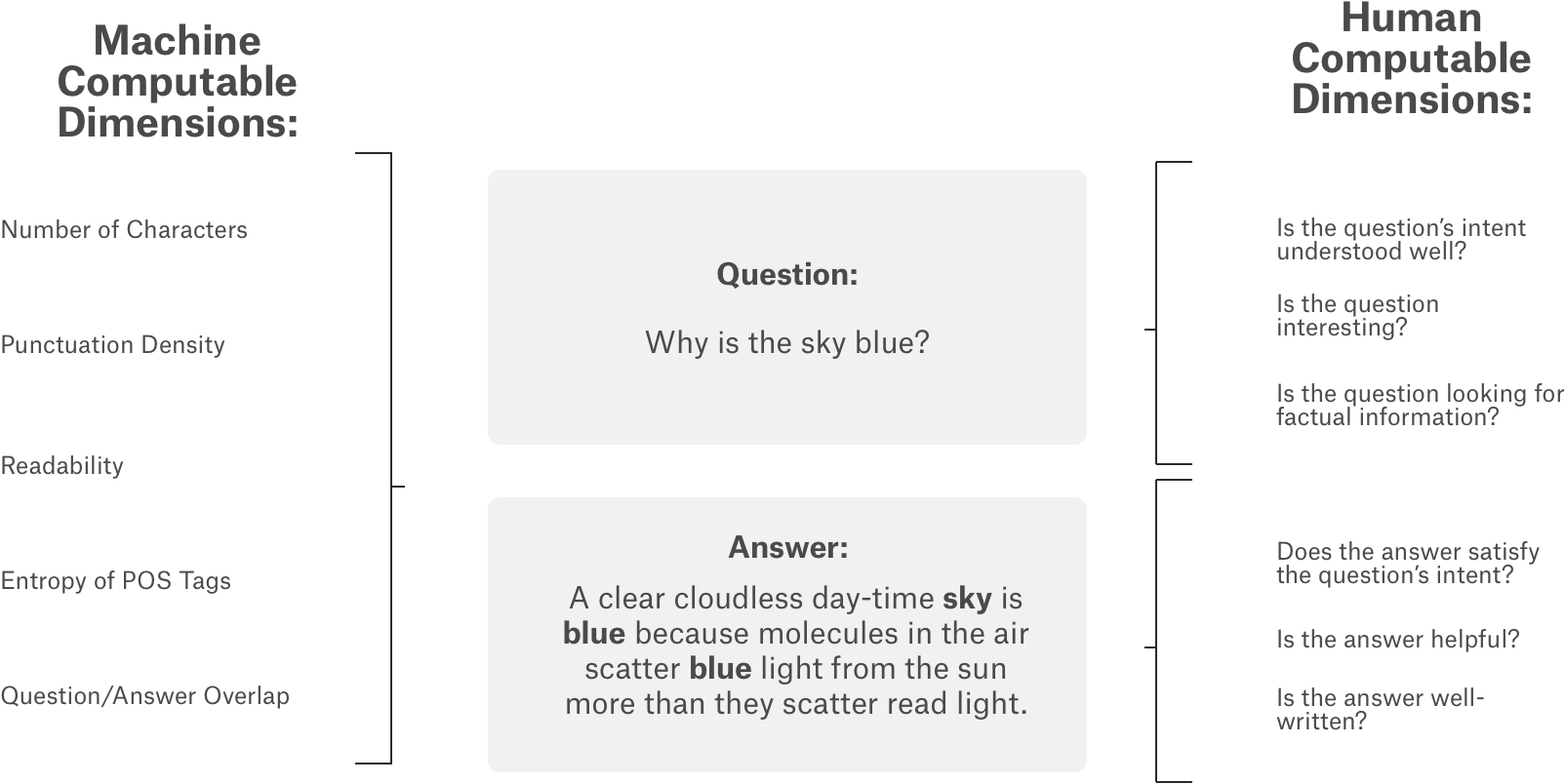
In this challenge, the objective is to predict different subjective aspects of question-answering gathered from different StackExchange properties. In this competition, we explored BERT model and hand picked feature engineering to develop a robust model that can predict the subjectivity metrics accurately.
|
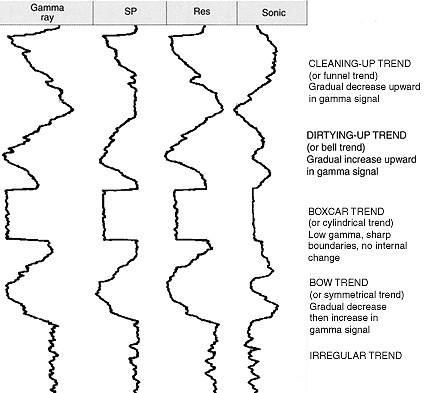
Image Credits: Link |
Given an array of GR (Gamma-Ray) values, accurately predict the log facies type corresponding to each value. Solution includes stacking of several seq2seq models with attention. Achieved overall 96.8% accuracy.
|

Image Credits: Link |
The challenge was to classify orientation of building roofs using satellite images of roof tops. We used different image augmentation techniques along with VGG network and achieved 82% accuracy on test dataset.
|
|
|
|
Joint topic-sentiment models aka. aspect rating models can extract thematic representation from texts at a granular level. In the areas of customer relationship management, it is utmost important to understand the pain point areas of customers from their feedbacks, complaints data and other data sources. By leveraging both sentiment as well as, thematic information, JST based models can understand the intent at overall level as well as, at theme level, which makes it perfect for analyzing voice of the customers.
|
|
|

|
Advisors: Dr. Tanmoy Chakraborty Leading Parmanu (Atomic) project on efficient large language models within LCS2 lab. |

|
Advisors: Dr. Tanmoy Chakraborty and Dr. Md. Shad Akhtar Courses: Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Social Network Analysis, Data Mining, Artificial Intelligence, Bayesian Machine Learning |

|
Courses: Algorithms, Machine Learning, Multivariate Analysis, Complex Networks, Information Retrieval, Econometrics, Statistical Inference |

|
Advised by Prof. Anupam Saikia for masters thesis on Mathematics of Elliptic Curves and its application in Cryptography Courses: Algorithms, Logic Programming (Prolog, Introduction to AI), Probability Theory, Numerical Analysis, Optimization |

|
Courses: Mathematical Logic, Algorithm Design, Game Theory, Theory of Computation, Programming |
|
|
Thanks to Jon Barron and Bodhisattwa P. Majumder for this nice template. |